How to connect to an SQL database on a remote server
October 08, 2020
Introduction
I started using PostgreSQL for a project recently. For deployment of that project, as usual, I am using dokku in a VPS. This quick guide will explain how to create a PostgreSQL database in dokku and how to connect to it from your PC using pgAdmin.
Hands-on
Creating a database in dokku
In order to use Postgres in dokku, a separate postgres plugin is needed. To install it, run the following command:
sudo dokku plugin:install https://github.com/dokku/dokku-postgres.git postgresCreating postgreSQL service for dokku
There is an official dokku plugin for MongoDB. We can install it by running:
dokku plugin:install https://github.com/dokku/dokku-mongo.git mongo
When the installation of the service has been completed, we can proceed to creating the database itself.
dokku postgres:create my-postgresmy-postgres being the name of the service.
The output of the command should be something like this:
user@my-server:~# dokku postgres:create my-postgres
Waiting for container to be ready
Creating container database
Securing connection to database
=====> Postgres container created: my-postgres
=====> my-postgres postgres service information
Config dir: /var/lib/dokku/services/postgres/my-postgres/data
Data dir: /var/lib/dokku/services/postgres/my-postgres/data
Dsn: postgres://postgres:9686c61f6a30562ac3c1ae1e6cd43d6b@dokku-postgres-my-postgres:5432/my_postgres
Exposed ports: -
Id: 3503897d4d50e7be6801ff900cfbc6ae919050d89043d4d2c1e927a0a9a83080
Internal ip: 172.17.0.11
Links: -
Service root: /var/lib/dokku/services/postgres/my-postgres
Status: running
Version: postgres:11.6The service is now successfully created.
By default the postgres service is using the port 5432 internally. If you take a look at the info output from the command above that you used for creating the database, you can see that Exposed ports entry is empty. To be able to connect to the database externally, we need to expose a port. We do this by running the following command:
dokku postgres:expose my-postgresThe command outputs the newly exposed port:
user@my-server:~# dokku postgres:expose my-postgres
-----> Service my-postgres exposed on port(s) [container->host]: 5432->20265The port is random, but you can define it also yourself by adding it at the end of the expose command. For example:
dokku postgres:expose my-postgres 29999Now our database is accessible from outside.
Connecting to the remote postgreSQL database from pgAdmin
Let’s first open up pgAdmin. I am using version 4.24 when writing this.
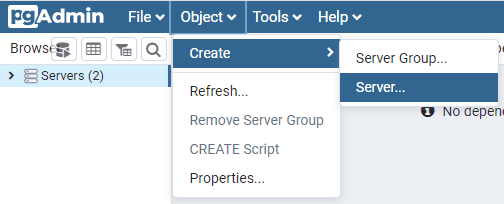
Select from the top tool bar Select - Create - Server….
In the server creation popup in the General tab we need to define the name of the database. This can be whatever you want. For clarity, I am using my-postgres, which is the name of the service we created before.
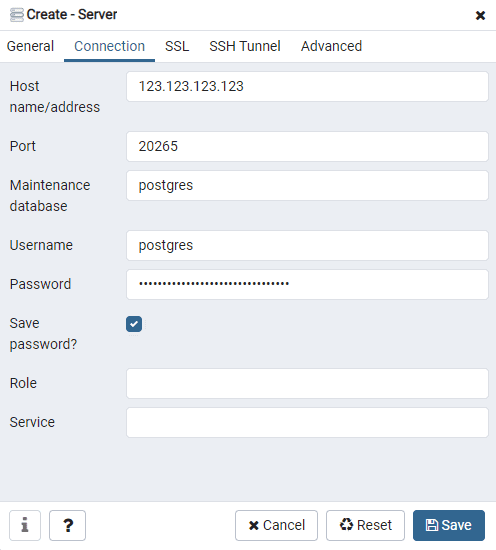
Then switch to Connection tab and fill in the following fields:
- Host name/address - Your servers host name or IP address
- Port - The port we exposed earlier
- Username - postgres (default)
- Password - The password part from the DNS
If you missed the info output when creating the database, you can request it by running the following command:
dokku postgres:info my-postgresThe password part of DSN is highlighted in the image below.
After filling up the information, we can just click Save and pgAdmin connects to the database. It can be found in the server browser on the left.
Conclusion
That’s all. Now you can easily access your postgreSQL database from your computer and do whatever you need to do with it.
Now that you have exposed a port in your server for the database, you can access it from other software as well. A common use case could be that you need to run a sript that populates the database when it’s first created or run some other one-off maintenance stuff. It could be anything. You will know it when you need it.
Thanks for reading!